Members: Robert Collins and Yanxi Liu
Past Members: Mark Wolff, Jingchen Liu, Minwoo Park, and Kyle Brocklehurst
Collaborators: Arthur Robert Pope, Vivek Verma, Stephen Charles Hsu, Mei Han, Vivek Kwatra, Grant Schindler, Panchapagesan Krishnamurthy, Roberto Lublinerman, Frank Dellaert, Jiebo Luo, Thommen Korah, Varsha Hedau, Vasu Parameswaran, Radek Grzeszczuk
Publications
M. Wolff, R. T. Collins and Y. Liu. Regularity-driven Facade Matching between Aerial and Street-Views, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2016 (Spotlight Presentation).J. Liu and Y. Liu, 'Local Regularity-driven City-scale Facade Detection from Aerial Images', Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2014. [PDF, Slides]
J. Liu, T. Korah, V. Hedau, V. Parameswaran, R. Grzeszczuk and Y. Liu, 'Entrance Detection from Street-View Images', Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshop 2014. [PDF]
M. Park and J. Luo and R. T. Collins and Y. Liu, 'Estimating the Camera Direction of A Geotagged Image using Reference Images', Pattern Recognition Journal 2014. [PDF]
M. Park, K. Brocklehurst, R.T. Collins and Y. Liu, 'Translation-Symmetry-based Perceptual Grouping with Applications to Urban Scenes', Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) 2010. [PDF, poster, MOVIE]
M. Park, K. Brocklehurst, R.T. Collins and Y. Liu, 'Deformed Lattice Detection in Real-World Images using Mean-Shift Belief Propagation', IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) 2009. [PDF]
M. Park, R.T. Collins and Y. Liu, 'Deformed Lattice Detection via Mean-Shift Belief Propagation' , European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2008. [PDF]
G. Schindler, P. Krishnamurthy, R. Lublinerman, Y. Liu and F. Dellaert, 'Detecting and Matching Repeated Patterns for Automatic Geo-tagging in Urban Environments', Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2008. [PDF]
Regularity-driven Facade Matching between Aerial and Street-Views
M. Wolff, R. T. Collins and Y. Liu. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2016 (Spotlight Presentation).
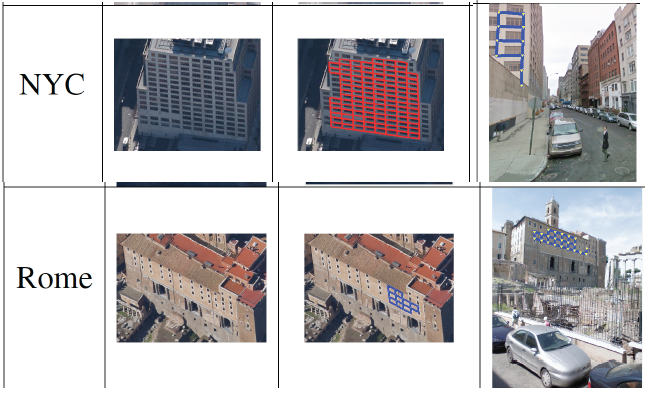 |
Local Regularity-driven City-scale Facade Detection from Aerial Images
J. Liu and Y. Liu. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2014 (Spotlight Presentation). [PDF, Slides]
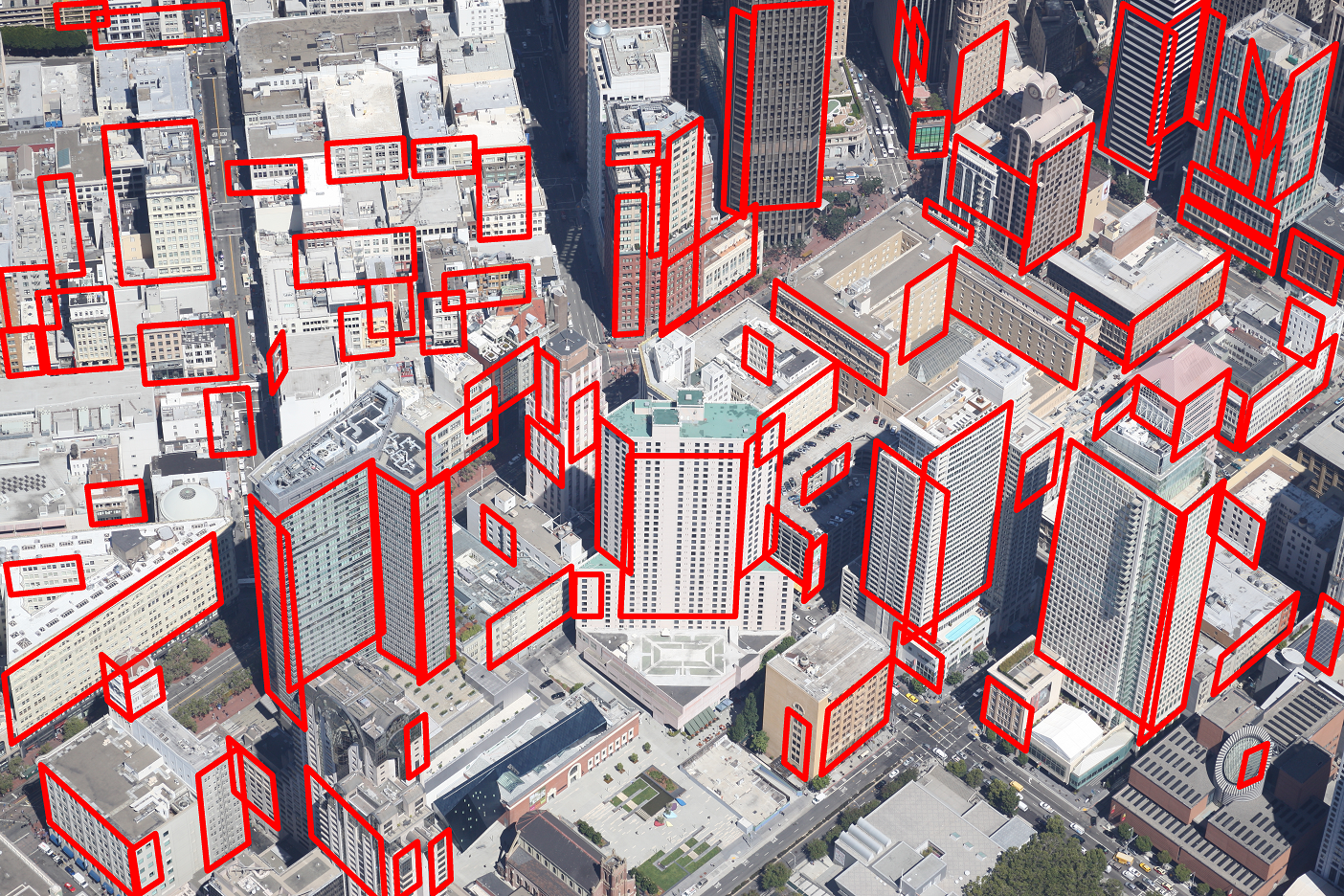 | 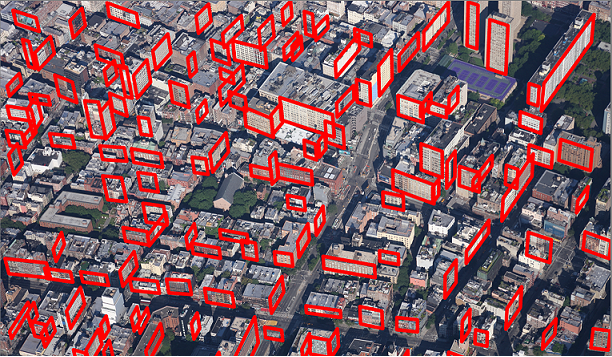 |
Abstract
We propose a novel regularity-driven framework for facade detection from aerial images of urban scenes. Gini-index is used in our work to form an edge-based regularity metric relating regularity and distribution sparsity. Facade regions are chosen so that these local regularities are maximized. We apply a greedy adaptive region expansion procedure for facade region detection and growing, followed by integer quadratic programming for removing overlapping facades to optimize facade coverage. Our algorithm can handle images that have wide viewing angles and contain more than 200 facades per image. The experimental results on images from three different cities (NYC, Rome, San-Francisco) demonstrate superior performance on facade detection in both accuracy and speed over state of the art methods. We also show an application of our facade detection for effective cross-view facade matching.
Cross-view Matching
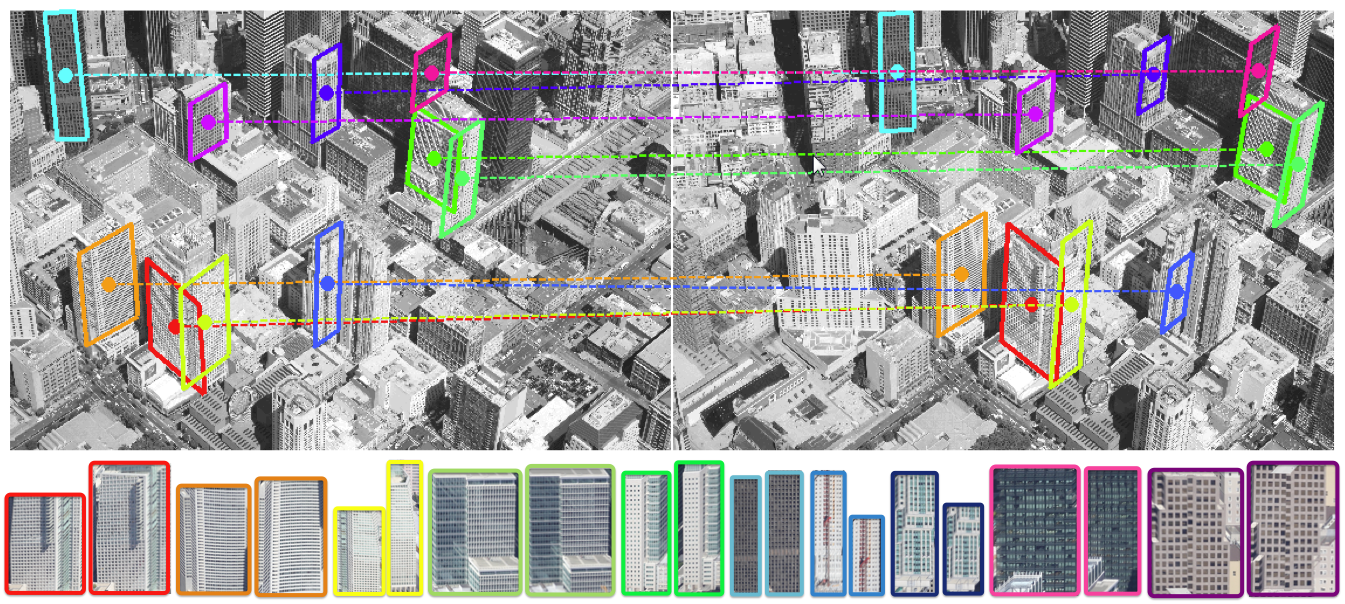 |
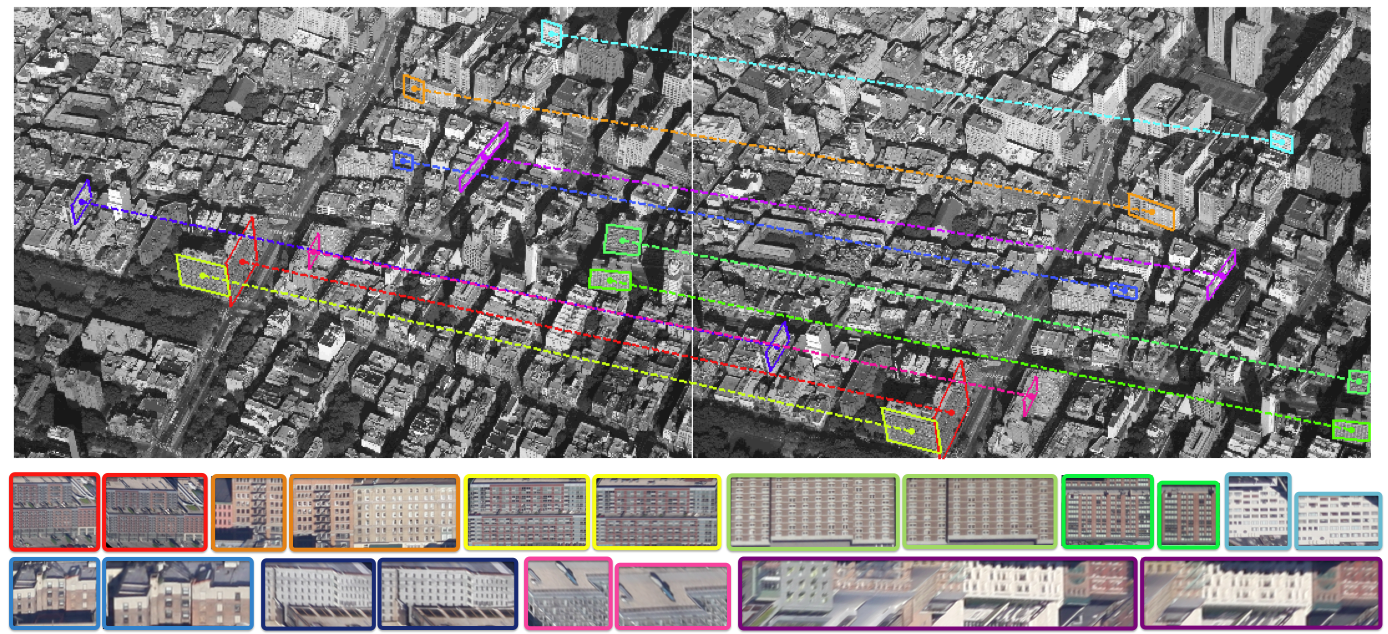 |
Demo Videos
Entrance Detection from Street-View Images
J. Liu, T. Korah, V. Hedau, V. Parameswaran, R. Grzeszczuk and Y. Liu. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshop 2014. [PDF]
 |
Abstract
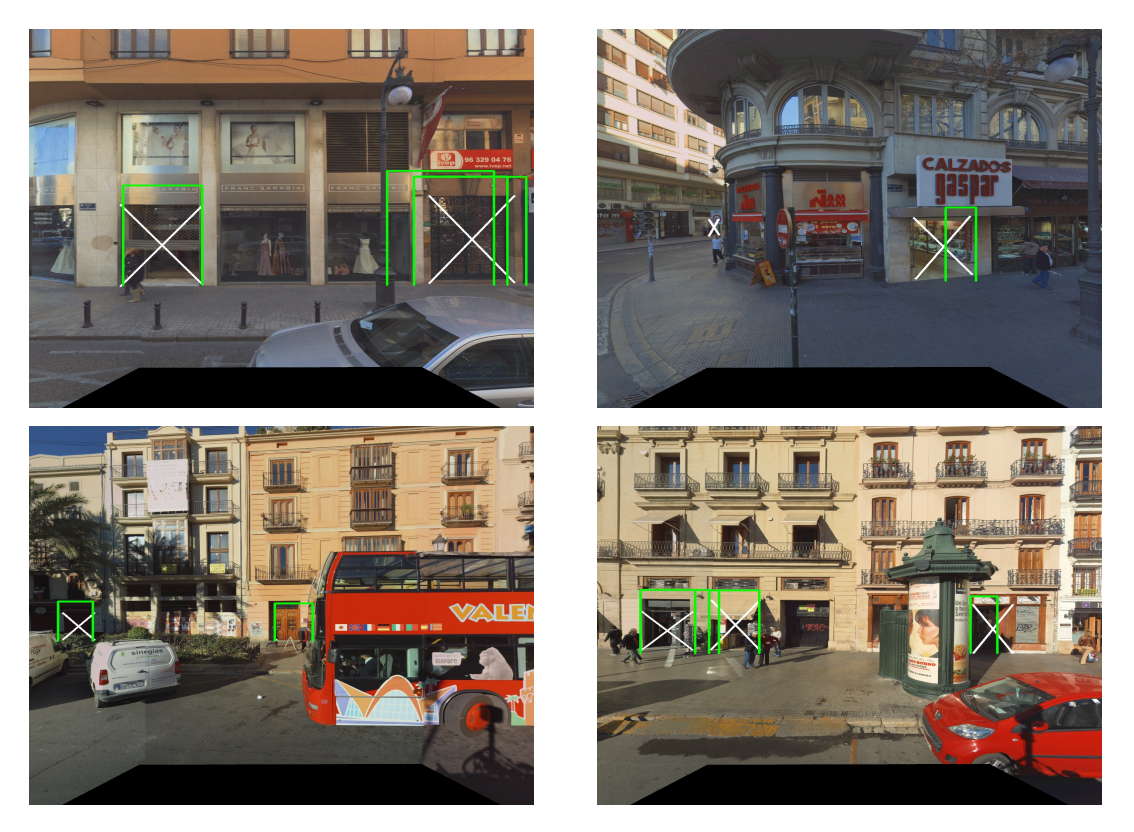
We present a system for detecting building entrances in outdoor scenes, an important problem for urban scene understanding. While entrance detection in indoor scenes has received a lot of attention, tackling the problem in outdoor scenes is considerably more complicated and remains largely unexplored. The wide variety of door appearances and geometries, background clutter, occlusions, specularity, and other difficult lighting conditions together impose many challenges. In this paper, we propose a three stage system that starts with a high-recall entrance candidate extractor. The next stage classifiers candidates based on local image features. The final stage fuses results from multiple views by using MCMC to solve a Bayesian inference problem, and to select the best set of entrances that explain the image of a facade. We achieve a precision of 70% at a recall of 70% on a challenging dataset of urban scene images. We will release this benchmark dataset to the public to facilitate future research on this topic.
Translation-Symmetry-based Perceptual Grouping with Applications to Urban Scenes
M. Park, K. Brocklehurst, R.T. Collins and Y. Liu. Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) 2010. [poster,PDF,MOVIE]
An important finding in our understanding of the human vision system is perceptual grouping, the mechanism by which visual el- ements are organized into coherent groups. Though grouping is generally acknowledged to be a crucial component of the mid-level visual system, in computer vision there is a scarcity of mid-level cues due to computational difficulties in constructing feature detectors for such cues. We propose a novel mid-level visual feature detector where the visual elements are grouped based on the 2D translation subgroup of a wallpaper pattern. Di erent from previous state-of-the-art lattice detection algorithms for near-regular wallpaper patterns, our proposed method can detect multi- ple, semantically relevant 2D lattices in a scene simultaneously, achieving an e ective translation-symmetry-based segmentation. Our experimen- tal results on urban scenes demonstrate the use of translation-symmetry for building facade super-resolution and orientation estimation from a single view.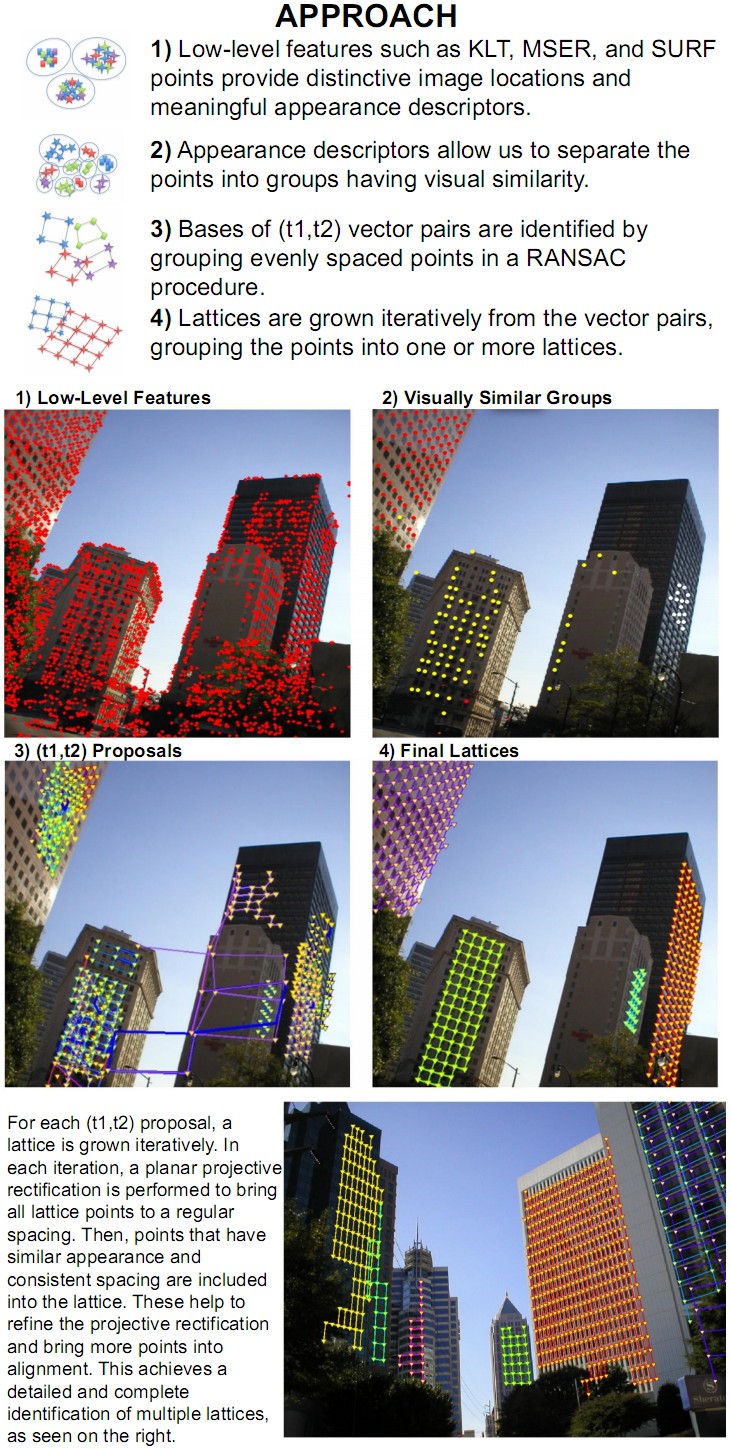
Deformed Lattice Detection in Real-World Images using Mean-Shift Belief Propagation
M. Park, K. Brocklehurst, R.T. Collins and Y. Liu. IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) 2009. [PDF]
We propose a novel and robust computational framework for automatic detection of deformed 2D wallpaper patterns in real-world images. The theory of 2D crystallographic groups provides a sound and natural correspondence between the underlying lattice of a deformed wallpaper pattern and a degree-4 graphical model. We start the discovery process with unsupervised clustering of interest points and voting for consistent lattice unit proposals. The proposed lattice basis vectors and pattern element contribute to the pairwise compatibility and joint compatibility (observation model) functions in a Markov Random Field (MRF). Thus, we formulate the 2D lattice detection as a spatial, multitarget tracking problem, solved within an MRF framework using a novel and efficient Mean-Shift Belief Propagation (MSBP) method. Iterative detection and growth of the deformed lattice are interleaved with regularized thin-plate spline (TPS) warping, which rectifies the current deformed lattice into a regular one to ensure stability of the MRF model in the next round of lattice recovery. We provide quantitative comparisons of our proposed method with existing algorithms on a diverse set of 261 real-world photos to demonstrate significant advances in accuracy and speed over the state of the art in automatic discovery of regularity in real images.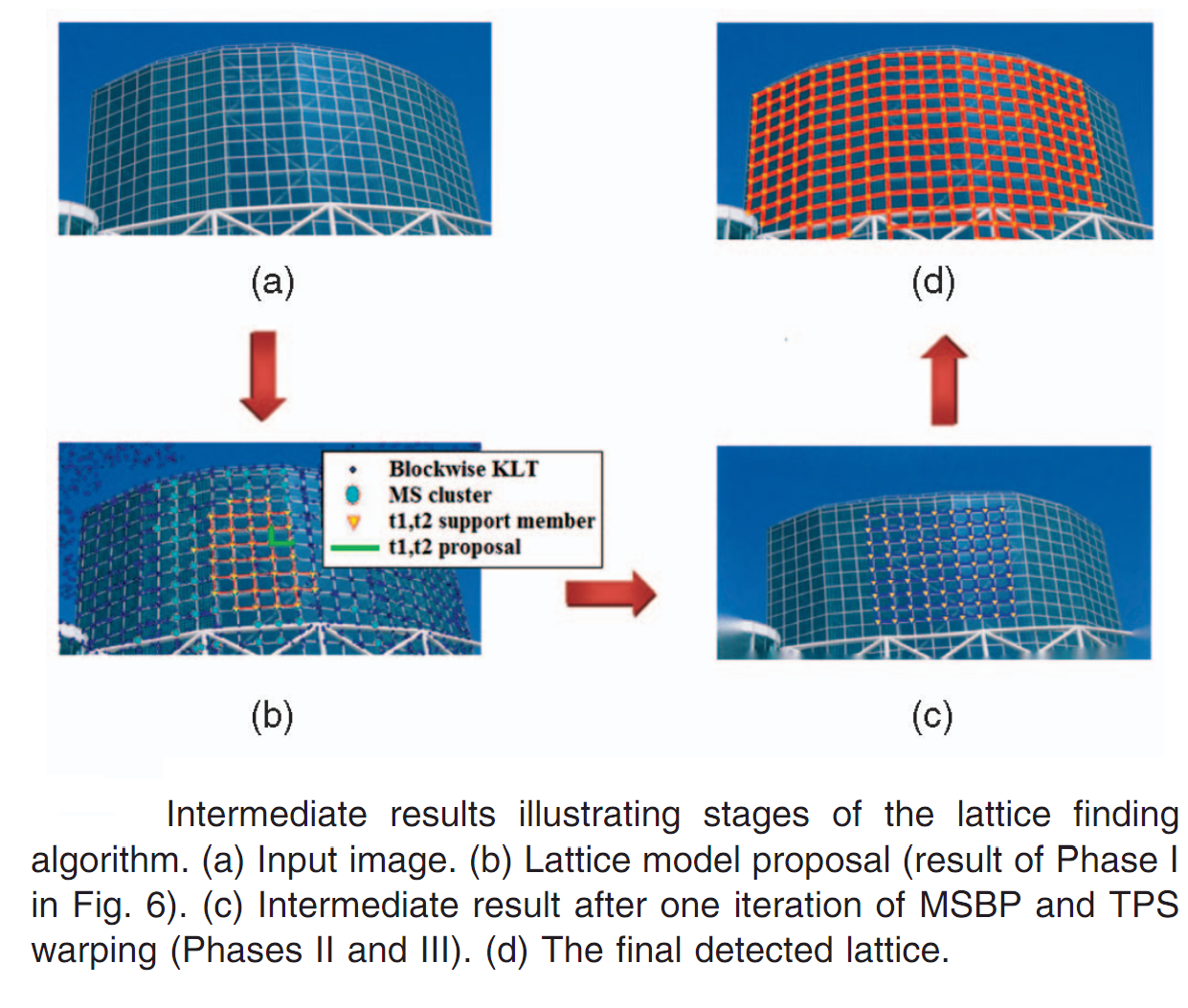
Detecting and Matching Repeated Patterns for Automatic Geo-tagging in Urban Environments
G. Schindler, P. Krishnamurthy, R. Lublinerman, Y. Liu and F. Dellaert. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2008. [PDF]
We present a novel method for automatically geo-tagging photographs of man-made environments via detection and matching of repeated patterns. Highly repetitive environments introduce numerous correspondence ambiguities and are problematic for traditional wide-baseline matching methods. Our method exploits the highly repetitive nature of urban environments, detecting multiple perspectively distorted periodic 2D patterns in an image and matching them to a 3D database of textured facades by reasoning about the underlying canonical forms of each pattern. Multiple 2D-to-3D pattern correspondences enable robust recovery of camera orientation and location. We demonstrate the success of this method in a large urban environment
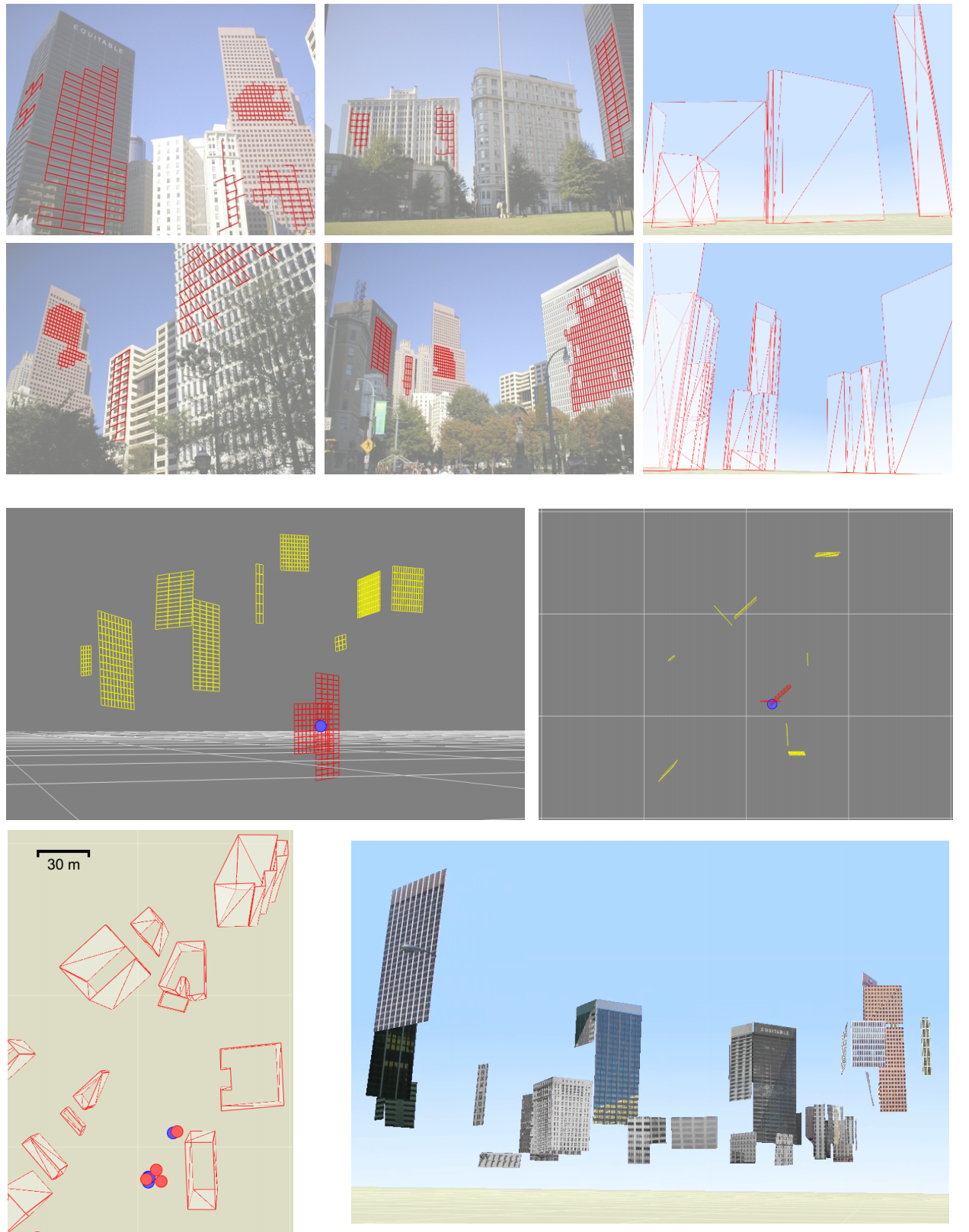
Acknowledgement
This work is funded partially under NSF grant IIS-1248076 and IIS-1144938, and a Google Faculty Award to Dr. Liu. We also thank Google for their urban scene image data sets.



